Environmentally friendly building materials. The requirements for construction materials
- Details
- Published: Thursday, 25 December 2014 10:41
- Written by UDK Gazbeton
 We live in an era of growing environmental crisis. Long-term imbalance in the nature of humanity is forced to realize that, despite their obviousness, for a long time escaped his attention: all the living organisms that inhabit our planet, do not exist by themselves, but depend on the environment and experiencing its effects. It should be recognized that in the field of environmental protection, we have advanced a little further than 50 years ago. By providing new construction, we have to realize that every building should not only meet the functional and aesthetic requirements, but does not have negative environmental impacts on the environment. What we build today must and after many years to harmonise with nature, and should not pollute it.
We live in an era of growing environmental crisis. Long-term imbalance in the nature of humanity is forced to realize that, despite their obviousness, for a long time escaped his attention: all the living organisms that inhabit our planet, do not exist by themselves, but depend on the environment and experiencing its effects. It should be recognized that in the field of environmental protection, we have advanced a little further than 50 years ago. By providing new construction, we have to realize that every building should not only meet the functional and aesthetic requirements, but does not have negative environmental impacts on the environment. What we build today must and after many years to harmonise with nature, and should not pollute it.
Typically, economical life of the building estimated for 80 years, and the functional life is for 40-50 years. After the end of the life of the building is demolished, and the question of waste disposal of the material with the possibility of recycling and reuse arises. Building materials, products and structures are up to 50-60% of construction costs. Choosing an effective resource and energy saving, environmentally friendly building materials, products and structures will reduce significantly the cost of construction, its labor and energy consumption while increasing the durability, quality and comfort of buildings, as well as significantly reduce the negative environmental impact on nature.
Raw materials for production of building materials should be widespread and environmentally friendly material. Among such natural materials are water, sand and carbonate rocks (limestone, chalk, marl) and their products – lime and cement. For example, in Russia the average value of the specific natural radionuclides limestone – 22.4 Bq/kg of sand – 40.3 Bq/kg, clay – 102,2 Bq/kg and granite – 126.8 Bq/kg. Multilateral analysis of the radiation safety of raw materials and building products shows the advantages of using residential construction products made of autoclaved aerated concrete. His background radiation is several times lower than that of the ceramic bricks and heavy concrete using crushed granite (material with a high content of natural radionuclides).
Consumption of raw materials per unit of production should be relatively small to ensure a minimum consumption of materials production. The energy intensity of production of building materials themselves should be minimized to reduce the production of raw materials for the production of heat and power, and reduce emissions into the atmosphere of carbon monoxide.
According to the Federal Association of manufacturers of sand-lime brick (Germany) for the production of 1 m3 of aerated concrete total energy consumption by an average of 324.11 kWh/m3 and hollow ceramic bricks – 616 kWh/m3.
Product Features cellular concrete
Huge analytical work on the technical and economic evaluation of various building materials has shown that the construction of cellular concrete in terms of materials, energy consumption, capital intensity and overall complexity compare favorably with traditional wall materials. For example, the specific capital investments, taking into account the associated costs for the production of raw and auxiliary materials and energy resources, for the walls of aerated concrete is 1.5 times less than that of the expanded clay.
The energy intensity of production (including production of binders and fillers) cellular concrete panels in comparison with the lightweight aggregate panels less than about 2 times, and cellular concrete building blocks in the 1.8-2.7 times less than the production of clay tiles and clay bricks and heat consumption; operating such buildings (per 1 m2 of the wall) less than 10-40%. The use of cellular concrete blocks in the brick walls of the buildings instead of bricks reduces the complexity of building in 1.4-2.0 times.
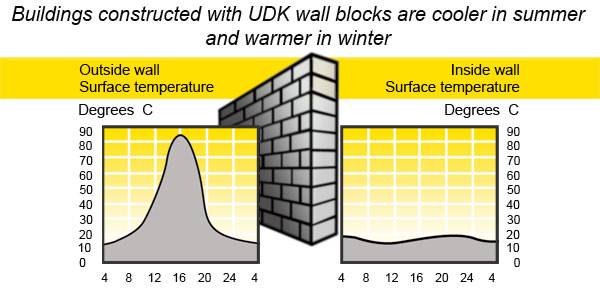
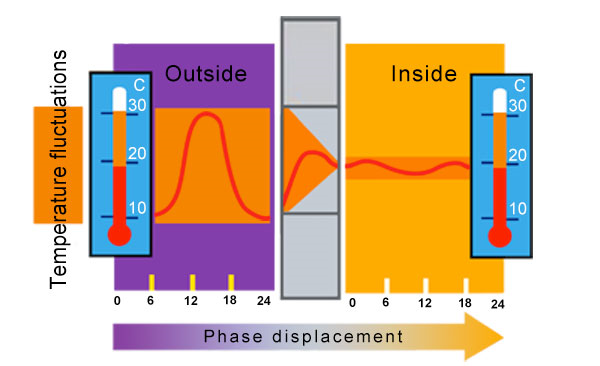
With the introduction of the new CIS standard indicators for thermal protection of buildings of the construction of the traditional wall materials (brick and lightweight aggregate panels) became uneconomical, as required to increase the thickness of the walls up to 1.5-2.0 m. The products of cellular concrete have a coefficient of thermal conductivity 2-3 times lower than that of brick and lightweight aggregate concrete panels. Accordingly, the walls of aerated concrete in 2-3 times warmer than the brick, while maintaining the thickness of the wall construction within 400-600 mm. This is advantageous, primarily for economic reasons, since the volume of the wall structures is also reduced by 2-3 times, while ensuring a thermal resistance corresponding to the new regulations.
In this situation, the accelerated development of the production of aerated concrete as the most effective, and virtually no alternative for the industrial-scale construction-insulating material is an urgent task. Considering that the volume of aerated concrete in the wall structure can be 70-100%, while increasing the volume of its production will significantly reduce overall labor costs, construction costs and, consequently, the market value of housing, while ensuring the new standard indicators of thermal performance of buildings.
In addition to assessing the technical and economic indicators of the effectiveness of using different wall materials and articles should mention another important factor – namely, microclimate of in-building atmosphere or the so-called amenities of accommodation. Grading comfort of human habitation in houses with walls made of different materials is known, the proposed foreign researchers International Symposium on autoclave construction materials in Hanover for more than 20 years ago. The first place for comfort, according to this gradation, occupied the house with walls made of wood, and then - at home with walls made of aerated concrete, then – the walls of silicate and ceramic brick, and the walls of conventional concrete and expanded clay in last place. Walls with mixed wall materials and products occupy the intermediate space in this graduation. As seen from the data on environmental indicators cellular concrete is closest to the wooden structures. Using autoclaved aerated concrete in buildings can reduce the amount of background radiation in the premises. It’s particularly topical for the regions of Belarus, Russia and Ukraine affected by the Chernobyl accident. Porous concrete "breathe" adjusting the humidity in the room. Structures of aerated concrete are practically eternal, and strength characteristics over time increase. Unlike wood, they do not rot, and both have properties close to the wood and stone.
Surveys homes with designs from cellular concrete, have served up to 60 years, showed the complete safety and suitability of the material for further use. Moreover, all types of walls of houses operated aerated are the warmest, which is energy efficient. Their equilibrium moisture content is 4 times less than the timber wall, the radioactivity is 5 times less than that of brick walls, vapor permeability (ability to "breathe") 3 times higher than that of wood, 5 – than the brick, 10 – than concrete sandwich panels.
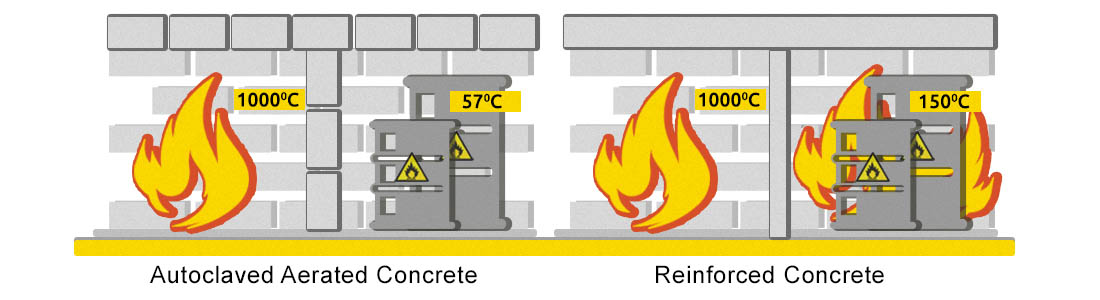
Cellular concrete relates to fireproof materials. It does not burn and effectively prevents the spread of fire and therefore can be used for walls of all classes of fire safety.
Based on materials from the publication: Experience the production and use of products autoclaved cellular concrete. The requirements for construction materials. Authors: T.G. Golubeva, N.P. Sazhnev, S.L. Galkin, N.N. Sazhnev